Virtual reality (VR) has transformed the way people experience digital content, immersing them in lifelike environments and interactive experiences. As technology evolves, the integration of 5G networks is set to revolutionize VR, enhancing its capabilities and accessibility. With lightning-fast speeds and low latency, 5G empowers users to explore virtual worlds without the frustrating lags and interruptions that once plagued online experiences.
This synergy between VR and 5G opens up a realm of possibilities, from gaming and education to virtual tourism and remote collaboration. As industries embrace this powerful combination, the future of immersive experiences looks brighter than ever. Understanding how VR and 5G work together is crucial for anyone interested in the next wave of technological advancements.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of VR and 5G
Virtual reality (VR) and 5G represent a significant advancement in digital technology. VR immerses users into realistic virtual environments, enhancing interaction and engagement. 5G, with its high-speed data transmission and minimal latency, supports seamless VR experiences.
Combining VR with 5G enhances the potential of immersive technologies. Users can access high-quality content with reduced lag, promoting real-time interactions. This synergy transforms experiences in several sectors, including:
- Gaming: Developers design more engaging VR games because 5G allows for complex graphics and rich environments.
- Education: Educators utilize VR to create interactive learning experiences, enabling students to explore subjects like history or science in a virtual setting.
- Virtual Tourism: Travelers can explore destinations virtually, offering immersive experiences that reduce the need for physical travel.
- Remote Collaboration: Teams can collaborate in virtual spaces, enhancing communication and productivity across distances.
The interplay between VR and 5G is crucial for driving innovation in these fields. Understanding this relationship highlights the future direction of technology and immersive experiences.
Benefits of VR and 5G Integration
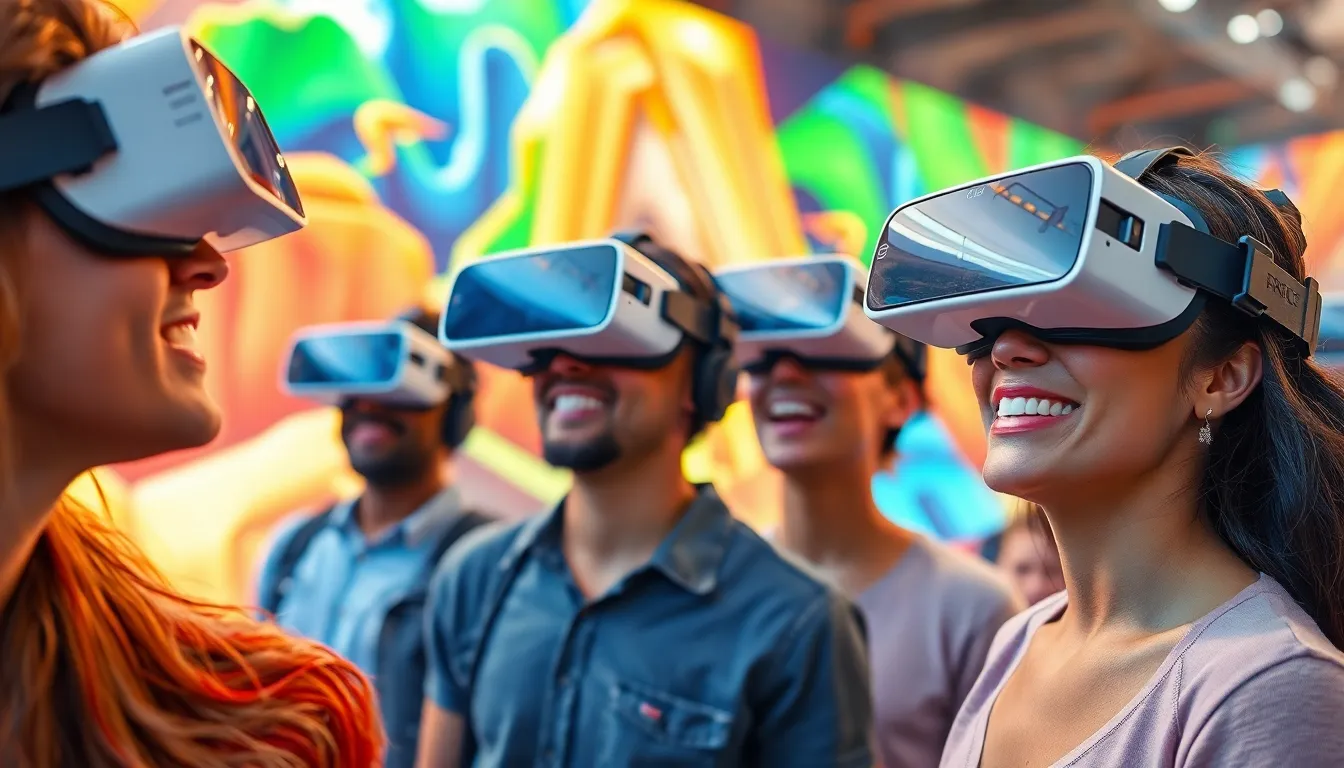

The integration of VR and 5G networks unleashes significant benefits, transforming user experiences across various applications. This synergy enhances interaction quality, fosters innovation, and expands possibilities in multiple fields.
Enhanced User Experience
Enhanced user experience emerges prominently with the integration of VR and 5G. With high-speed data transfer, users engage with rich multimedia content seamlessly. Immersive environments, such as detailed gaming worlds or lifelike educational simulations, rely on 5G’s capability to deliver high-resolution graphics instantly. Users experience less distortion and improved visuals, resulting in more captivating interactions. In virtual tourism, travelers enjoy real-time access to popular destinations, enhancing the exploration experience. Ultimately, this combination elevates user satisfaction, promotes engagement, and encourages prolonged use.
Reduced Latency
Reduced latency plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of VR applications. 5G technology dramatically decreases response times to mere milliseconds, allowing users to interact with virtual environments almost instantaneously. This rapid feedback loop leads to more natural interactions, whether in gaming or collaborative workspaces. In educational settings, timely reactions during immersive learning make content more intuitive, deepening understanding. With reduced latency, VR reality feels more authentic, bridging the gap between real and virtual, thus solidifying user trust in the technology. This advancement not only enhances experiences but also sets a foundation for future innovations in VR applications.
Key Technologies Supporting VR and 5G
Several key technologies underpin the integration of VR and 5G, enhancing performance and user experiences. Notably, edge computing and cloud services play pivotal roles in this innovative landscape.
Edge Computing
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, allowing VR content to load and respond more quickly. By minimizing the distance data must travel, it enables real-time interactions in virtual environments. This technology supports applications where instantaneous feedback is crucial, such as multiplayer gaming or VR simulations. Through dedicated edge servers, users can experience smoother graphics and less interruption. Just-in-time data transmission in edge computing significantly enhances the overall immersive experience, making virtual environments more responsive and engaging.
Cloud Services
Cloud services facilitate vast data storage and processing capability essential for VR applications. They support heavy computational tasks, allowing VR experiences to become more sophisticated without demanding extensive local processing power. With scalable infrastructure, cloud services enable developers to create complex environments that adjust to user behaviors in real time. Furthermore, cloud storage ensures users can access their VR content from various devices, promoting portability and ease of use. The collaborative potential of cloud services enhances shared experiences, where multiple users interact seamlessly in the same virtual environment, fostering community and collaboration.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promising combination of VR and 5G, several challenges and limitations hinder optimal integration. Addressing these obstacles is essential for realizing the full potential of these technologies.
Technical Barriers
Technical barriers significantly affect the deployment of VR and 5G. Network infrastructure often lacks the necessary coverage, particularly in rural areas, creating connectivity gaps that disrupt user experiences. VR applications demand substantial data throughput and processing power; insufficient bandwidth can lead to lag, stuttering visuals, and overall diminished immersion. Additionally, the fragmentation of standards across VR platforms complicates compatibility, making it challenging for developers to deliver seamless experiences across devices. These technical hurdles must be overcome to ensure widespread adoption and user satisfaction.
Cost Implications
Cost implications create another layer of complexity in the adoption of VR and 5G technologies. The expenses associated with developing high-quality VR content can be significant, including investments in hardware and software, skilled labor, and ongoing maintenance. Similarly, the rollout of 5G infrastructure entails substantial costs for telecommunications companies, which may lead to higher consumer prices for access to enhanced services. Users may resist transitioning to 5G networks due to these increased costs, limiting the reach of VR applications. Addressing these financial challenges is crucial for promoting broader adoption in both consumer and enterprise markets.
Future of VR and 5G
The future of VR and 5G signals a transformative shift in digital experiences, focusing on enhanced connectivity and immersive content. This evolution holds exciting prospects for a range of industries.
Expected Developments
Anticipated advancements in VR and 5G technology include enhanced hardware capabilities and improved software optimization. Improved VR headsets, equipped with higher resolution displays and better tracking systems, aim to deliver more realistic experiences. Integration of AI-driven algorithms will enhance content personalization, creating tailored user interactions. Moreover, ongoing expansion of 5G infrastructure is expected to reduce coverage gaps, particularly in rural areas, facilitating wider access to high-speed connectivity. Continuous collaboration between telecom providers and VR developers will drive the push towards real-time, multi-user environments.
Potential Applications
Numerous potential applications of VR and 5G span across diverse sectors.
- Gaming: Developers can create multiplayer environments with lifelike graphics and real-time interactions, bridging gaps between players worldwide.
- Education: VR offers immersive learning experiences, allowing students to explore historical events or scientific concepts firsthand, fostering engagement and retention.
- Healthcare: Medical professionals can use VR for training simulations, while patients benefit from therapy applications that reduce anxiety and stress.
- Retail: Virtual showrooms enable customers to experience products in an interactive 3D space before purchase, enhancing decision-making.
- Virtual Tourism: Users can explore global destinations through guided VR experiences, providing a sense of presence while remaining comfortable at home.
- Remote Collaboration: Teams can conduct meetings in a shared virtual space, improving communication and collaboration with a realistic presence.
These applications emphasize the synergy between VR and 5G, enabling deeper engagement and enriching user experiences across various domains.
The convergence of VR and 5G is set to redefine how individuals interact with digital content. As these technologies evolve together, they promise to create more immersive and engaging experiences across various sectors. The potential for enhanced connectivity and real-time interactions opens doors to innovative applications that were once thought impossible.
While challenges remain in terms of infrastructure and cost, the ongoing advancements in both VR and 5G will likely address these hurdles. As the landscape continues to shift, users can expect richer experiences that not only entertain but also educate and connect people in new ways. The future of VR and 5G is bright, paving the way for a more interactive and immersive digital world.