In the world of 3D printing, layer height is the unsung hero that can make or break a project. Imagine crafting a masterpiece only to find it looks like a lumpy potato instead of a sleek design. Layer height isn’t just a number; it’s the secret sauce that determines the quality and finish of your prints.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Layer Height in 3D Printing
Layer height refers to the thickness of each layer in 3D printing. It significantly impacts print quality, detail, and overall aesthetics.
What is Layer Height?
Layer height measures the vertical distance between each printed layer. Common layer heights range from 0.1 mm to 0.3 mm, depending on the printer and material. A smaller layer height results in finer details, while a larger height speeds up printing time. Various slicers support settings for custom adjustments to achieve desired outcomes. Understanding this metric is crucial for optimizing print designs.
Importance of Layer Height
Layer height directly influences the final print quality. A smaller layer height enhances detail, making it suitable for intricate models. Larger heights reduce print time but may sacrifice smoothness. Each print project requires careful consideration of layer height for a perfect finish. Users often balance speed and quality based on project needs and material characteristics. Selecting the appropriate layer height shapes the appearance and strength of the printed object.
Factors Affecting Layer Height
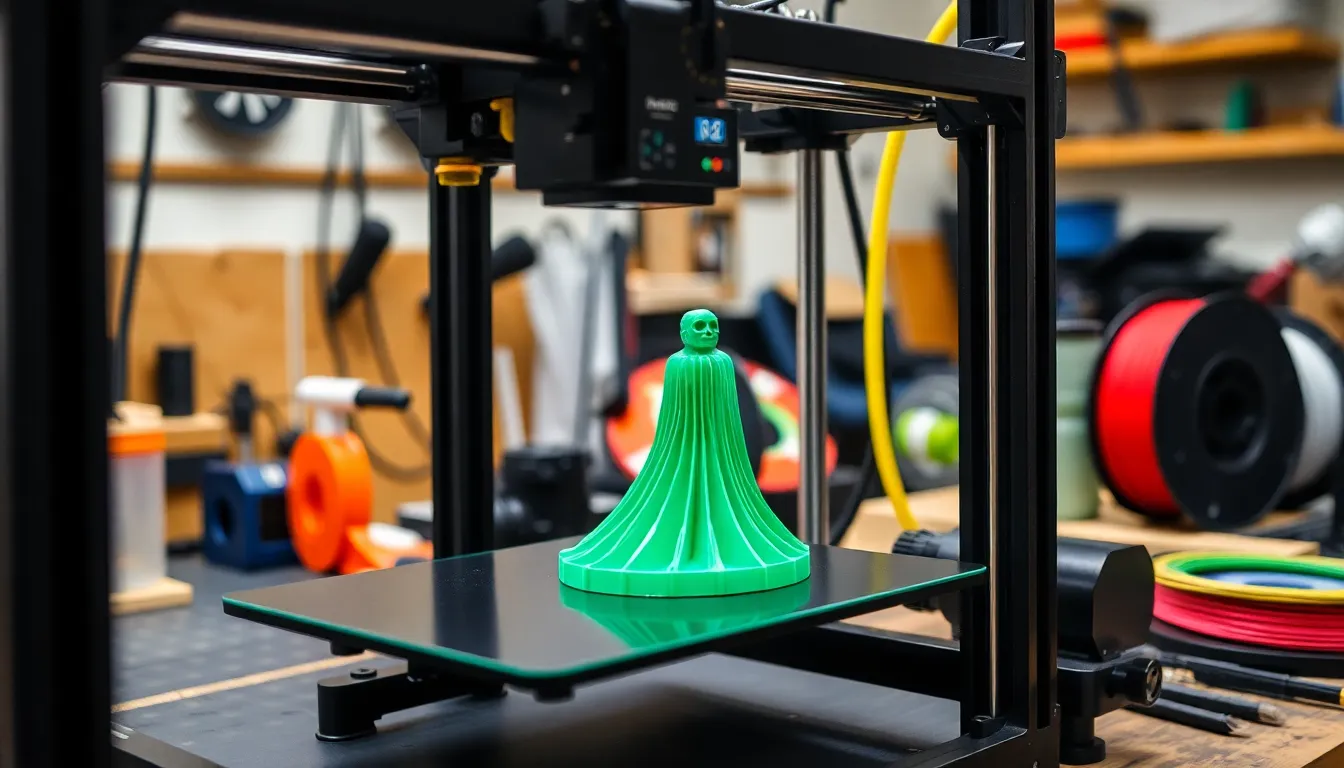

Layer height selection affects various printing characteristics. Multiple factors influence this critical decision, including printer type and material choice.
Printer Type and Settings
Printer type determines the optimal layer height for projects. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers usually cater to a layer height range from 0.1 mm to 0.3 mm. Users often find that resin printers benefit from lower layer heights due to their high-resolution capability. Settings like nozzle diameter, print speed, and temperature also impact layer performance. For instance, larger nozzles allow thicker layers, which can expedite the printing process. Calibration is essential; misconfigured settings can lead to defects in print quality.
Material Choice
Material selection significantly influences layer height preferences. Filaments such as PLA allow for smaller layer heights, producing detailed prints without layer adhesion issues. On the other hand, ABS may require thicker layers for optimal results due to its warping tendencies. Each material’s viscosity affects how well layers bond together. Specialized materials, like flexible filaments, often necessitate different approaches, as they tend to perform better with larger layer heights to ensure consistent flow. Understanding the material characteristics aids in making informed layer height decisions.
Advantages of Different Layer Heights
The choice of layer height in 3D printing provides significant advantages, impacting both quality and efficiency of prints.
Fine Layer Height Benefits
Fine layer heights, typically ranging from 0.1 mm to 0.15 mm, enhance detail and precision. Models featuring intricate designs, like figurines or architectural features, exhibit exceptional smoothness and definition. Achieving a high level of finish becomes more straightforward, resulting in prints that require minimal post-processing. Fine layer heights also improve the overall appearance of small components with complex geometries. Users often prefer finer layers to capture the nuances in texture and shape, making them ideal for artistic projects.
Coarse Layer Height Benefits
Coarse layer heights, commonly between 0.2 mm and 0.3 mm, significantly reduce print times. Rapid production becomes feasible for larger objects, such as prototypes or functional parts, where fine detail is less critical. The speed of printing with coarse layers often aids users in projects with tight deadlines. These layers offer increased adhesion between layers, minimizing the risk of defects during printing. Coarse layer heights generally require less printer calibration and can enhance overall material usage efficiency. For functional applications where aesthetics hold lesser importance, coarse layers deliver a practical and effective solution.
Best Practices for Optimizing Layer Height
Choosing the right layer height involves careful adjustments to printer settings and ongoing experimentation.
Adjusting Settings for Quality
Precision in printer settings significantly influences print quality. Printer users should first calibrate the nozzle diameter to ensure optimal flow of material. Adjusting the print speed also plays a critical role; slower speeds generally enhance detail. Temperature settings require attention, as the extruder temperature impacts layer adhesion and overall finish quality. Users should select layer height based on specific project requirements; thin layers may need higher temperatures to prevent clogs. Ultimately, each adjustment contributes to achieving the desired surface smoothness and feature fidelity.
Experimentation and Testing
Testing various layer heights helps users find the best fit for their projects. Start with a few small test prints using different layer heights to evaluate the impacts of finer details versus print speed. Iteration is key; comparing the results will pinpoint which settings yield satisfying outcomes. Adjust as necessary based on printed models, noting differences in appearance and mechanical performance. Utilizing a systematic approach enables more informed decisions on final layer height selection. Prioritizing thorough testing ensures optimal prints that fulfill specific aesthetic and functional demands.
Choosing the right layer height in 3D printing is pivotal for achieving high-quality results. It influences not just the aesthetics but also the functionality of the printed object. By understanding the nuances of layer height selection users can tailor their prints to meet specific project requirements.
Experimentation with different settings and materials is essential for finding the optimal balance between detail and speed. As technology advances and materials evolve staying informed about best practices will ensure successful outcomes in 3D printing endeavors. Ultimately the right layer height can transform an ordinary print into an extraordinary one.