Imagine stepping into a world where rehabilitation feels less like a chore and more like an adventure. Virtual reality is revolutionizing stroke rehabilitation by transforming tedious exercises into engaging experiences. Gone are the days of monotonous therapy sessions—now, patients can embark on thrilling virtual quests while regaining their strength and mobility.
This innovative technology not only makes therapy fun but also enhances motivation and progress. Picture this: instead of lifting weights, you’re battling dragons or exploring underwater realms. With virtual reality, the path to recovery takes a creative twist, making it easier for patients to stay committed to their rehabilitation journey. As the digital landscape evolves, so do the possibilities for recovery, proving that healing can be both effective and enjoyable.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Virtual Reality in Rehabilitation
Virtual reality (VR) enhances rehabilitation by immersing patients in interactive environments. These environments enable them to engage in therapeutic exercises tailored to their specific needs. By simulating real-life scenarios, VR allows users to practice movements that may be challenging in their daily lives.
Numerous studies indicate that VR increases patient motivation. Engaging elements, such as games and challenges, encourage patients to participate actively. Patients often complete more repetitions in a shorter time compared to traditional therapy.
Research underscores VR’s effectiveness with various rehabilitation goals, particularly for stroke survivors. Improvements in motor skills, coordination, and spatial awareness are commonly reported. VR applications can adjust difficulty levels based on individual progress, ensuring personalized therapy.
In addition to physical benefits, virtual reality provides emotional support. Patients experience reduced feelings of isolation and anxiety when using immersive environments. Community features often incorporate social interactions, fostering a sense of belonging.
Cost-effectiveness is another advantage of VR in rehabilitation settings. Instead of recurring therapy sessions, engaging VR programs can be utilized at home, reducing transportation expenses. Reliable data shows that patients participating in VR-based programs report faster recovery times and higher satisfaction levels.
VR technology continually evolves, expanding options for rehabilitation. Advancements include enhanced graphics, improved motion tracking, and interactive feedback systems. These innovations create a more compelling and responsive therapy experience for stroke survivors.
Virtual reality, therefore, transforms stroke rehabilitation into an engaging, efficient process, meeting the diverse needs of patients along their recovery journey.
Benefits of Virtual Reality for Stroke Rehabilitation
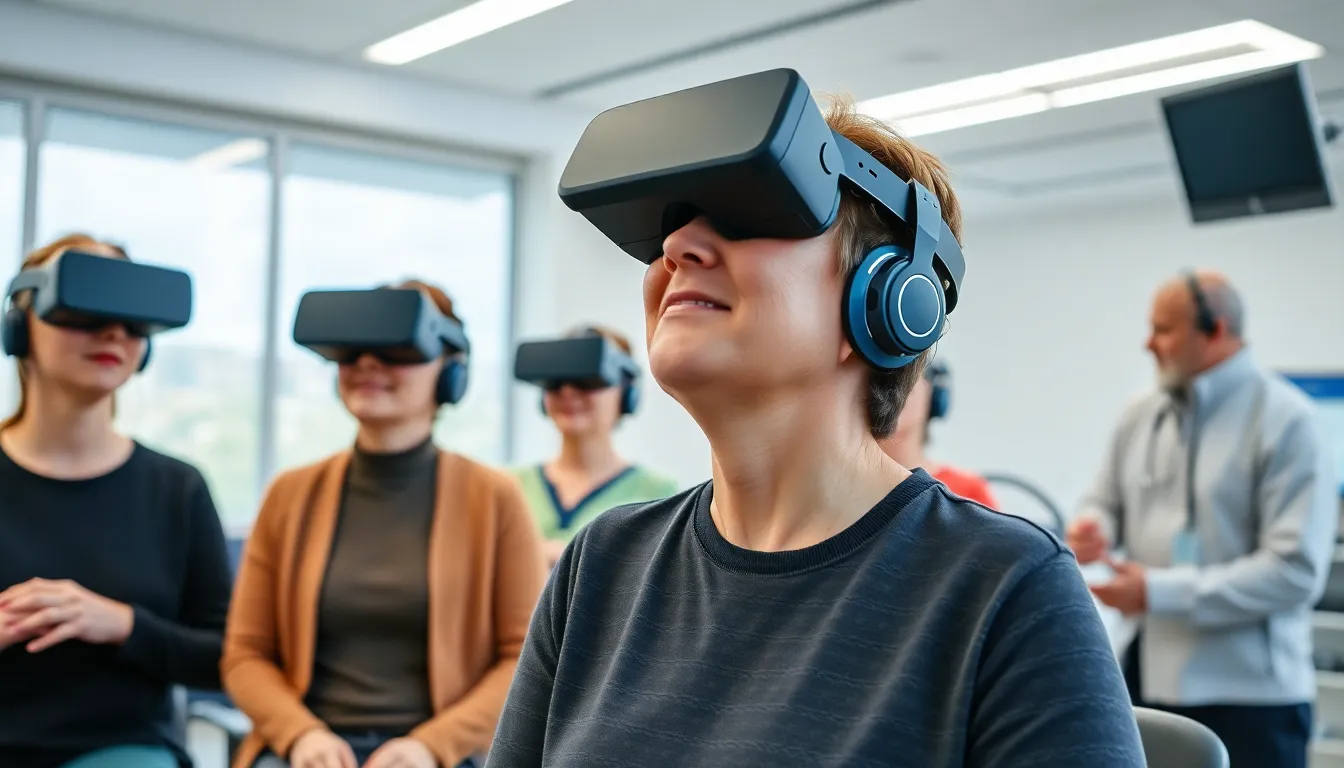

Virtual reality (VR) offers numerous advantages for stroke rehabilitation, fundamentally changing the approach to recovery. By making therapy enjoyable, VR enhances patient engagement and supports progress.
Enhanced Engagement
Engagement in therapy improves significantly with VR’s interactive environments. Patients interact with vibrant, immersive scenarios that hold their attention, making repetitive exercises feel less tedious. Gamified elements, such as rewards and challenges, motivate users to participate actively, leading to higher adherence rates. Research shows that enhanced engagement translates to a more enjoyable rehabilitation experience, encouraging patients to practice consistently. Patients are more likely to look forward to their sessions when they can escape into virtual worlds, creating a positive feedback loop that enhances their overall outcomes.
Improved Motor Function
Motor function improvement stands out as one of the key benefits of VR for stroke survivors. By practicing movements within a controlled virtual environment, patients can focus on specific tasks that challenge their motor skills. VR technology provides real-time feedback, allowing users to adjust their movements based on performance. Studies highlight significant gains in coordination and strength, ultimately leading to better functional independence. Adjusting the difficulty level within the VR programs enables personalized training that meets individual capabilities, ensuring targeted progress for each patient. Increased repetition also solidifies new motor patterns, further enhancing recovery prospects.
Current Technologies and Approaches
Virtual reality (VR) technology is revolutionizing stroke rehabilitation through innovative software applications and wearable devices. These advancements create engaging and effective therapy experiences for patients.
VR Software and Applications
Numerous VR applications target the specific needs of stroke survivors. Patients engage in immersive experiences that encourage movement and coordination. Popular programs include VR games that challenge users to complete tasks, enhancing motor skills while having fun. Research suggests that these gamified elements significantly improve user adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Engaging content helps reduce the monotony of traditional therapies, allowing patients to practice skills in a colorful, interactive environment. Developers continue to advance VR technologies, incorporating adaptive feedback mechanisms that tailor the experience to individual ability levels.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices enhance the effectiveness of VR rehabilitation programs. These devices often include sensors that monitor movement and provide real-time feedback. Stroke survivors can wear these devices during VR sessions to track progress and improve functionality. Some wearables also connect with VR software, creating synchronized experiences that allow for more comprehensive rehabilitation. Patients often find this integration motivates them to persist in their therapy. Combining wearables with VR technologies results in a holistic approach to recovery, supporting both physical and emotional well-being. As the field progresses, these devices become increasingly sophisticated, providing valuable data that helps tailor treatment plans.
Challenges and Limitations
Virtual reality provides exciting benefits in stroke rehabilitation, yet several challenges impede its widespread adoption.
Accessibility Issues
Accessibility remains a significant barrier in implementing VR solutions. Patients with limited mobility or those who experience severe cognitive impairment may struggle to benefit from these technologies. Cost can also be prohibitive. Not all rehabilitation facilities offer VR programs, limiting access for many stroke survivors. Furthermore, individuals without reliable internet connections encounter additional obstacles in utilizing at-home VR therapies. The need for specialized equipment also adds to the complexity, as not every patient has access to the necessary devices.
Research Gaps
Research gaps hinder the full understanding of VR efficacy in stroke rehabilitation. Existing studies often lack long-term follow-ups, making it difficult to assess the lasting impact of VR therapy. Diversity in study populations leads to inconsistencies in outcomes. Limited data exists on specific patient demographics, such as age or the severity of stroke, which may influence VR response. Additionally, variations in VR systems and protocols complicate comparisons among studies. As a result, more comprehensive research is vital to establish optimal practices and long-term benefits for stroke survivors.
Future Directions in Virtual Reality for Stroke Rehabilitation
Advancements in virtual reality (VR) technology are shaping the future of stroke rehabilitation. Improved graphics and motion tracking enhance user experiences, making therapy more immersive. New software applications continuously provide engaging ways for stroke survivors to practice essential movements. They deliver tailored rehabilitation programs that fit individual needs.
Innovative VR applications incorporate gamification, encouraging patients to achieve specific goals through interactive challenges. Such elements significantly boost motivation, helping individuals remain committed to their rehabilitation. Increased patient engagement results in improved motor function and coordination, essential for post-stroke recovery.
Collaboration between VR developers and rehabilitation professionals fuels the creation of specialized tools designed for stroke therapy. Integration of wearable devices further optimizes these programs, offering real-time feedback based on user movements. Such synergies strengthen the holistic approach to stroke recovery, supporting both physical capabilities and emotional health.
Emerging research is crucial in understanding the long-term effects of VR rehabilitation. Conducting comprehensive studies on diverse populations, including varied stroke severities and age groups, enhances the validity of findings. Prioritizing investigations into long-term outcomes allows for the establishment of best practices for VR therapy.
Addressing accessibility remains vital in ensuring equitable access to VR rehabilitation. Developers are focusing on designing programs that cater to individuals with limited mobility and cognitive impairments. Simplifying technologies and reducing costs could enhance availability in rehabilitation centers, transforming therapy accessibility for stroke survivors.
Ultimately, continuous innovation and consistent research provide significant opportunities to refine stroke rehabilitation practices. As the field evolves, the integration of VR into therapeutic protocols will likely enhance recovery outcomes and foster independence for stroke survivors.
Virtual reality is revolutionizing stroke rehabilitation by making therapy more engaging and effective. This innovative approach not only enhances patient motivation but also fosters significant improvements in motor skills and coordination. As technology advances the potential for personalized and immersive experiences continues to grow.
The integration of gamified elements and real-time feedback creates a supportive environment that encourages active participation. While challenges remain in terms of accessibility and research, the future of VR in stroke rehabilitation looks promising. Ongoing advancements will likely lead to even more tailored solutions for stroke survivors, ultimately paving the way for improved recovery outcomes and greater independence.