In a world where everything seems to be getting lighter and more flexible, titanium stands out as the superhero of metals. It’s strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant, making it a favorite in industries from aerospace to medical devices. But what happens when you throw 3D printing into the mix? You get a game-changer that’s revolutionizing how we think about manufacturing.
Imagine crafting intricate designs that were once impossible, all while sipping coffee in your pajamas. 3D printing titanium isn’t just a trend; it’s a powerful tool that’s reshaping production processes and pushing the limits of innovation. With this technology, the future of metalworking is not just bright—it’s downright dazzling! Buckle up as we dive into the fascinating world of 3D printed titanium and explore why it might just be the secret ingredient your next project needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing Titanium
3D printing titanium utilizes additive manufacturing techniques to produce components with unmatched precision. This process involves layers of titanium powder being fused together using a laser, allowing for intricate geometries impossible with traditional methods. Manufacturers leverage this technology to create lightweight yet strong structures that meet strict performance requirements.
Not only does it enhance design flexibility, but 3D printed titanium also results in reduced material waste compared to subtractive manufacturing methods. Companies experience shorter lead times as designs move from concept to production swiftly. Specific industries, such as aerospace, benefit significantly due to titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance.
The process can produce various parts, including brackets, gears, and medical implants, catering to distinct applications. Various titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-3Al-2.5V, often serve to improve performance characteristics for specific use cases. Each alloy offers unique benefits, making selection essential based on functional requirements.
Additionally, post-processing techniques can enhance surface finish and reduce residual stresses in titanium components. Treatments like heat treatment and surface polishing contribute to the quality of the final product. By embracing 3D printing, businesses not only streamline their manufacturing processes but also push the boundaries of what is achievable in engineering and design.
The future for 3D printing titanium appears bright. As technology advances, capabilities in producing more complex parts will increase, driving innovation across various sectors. Embracing these advancements means accessing endless opportunities to improve product design and functionality.
Benefits of 3D Printing Titanium
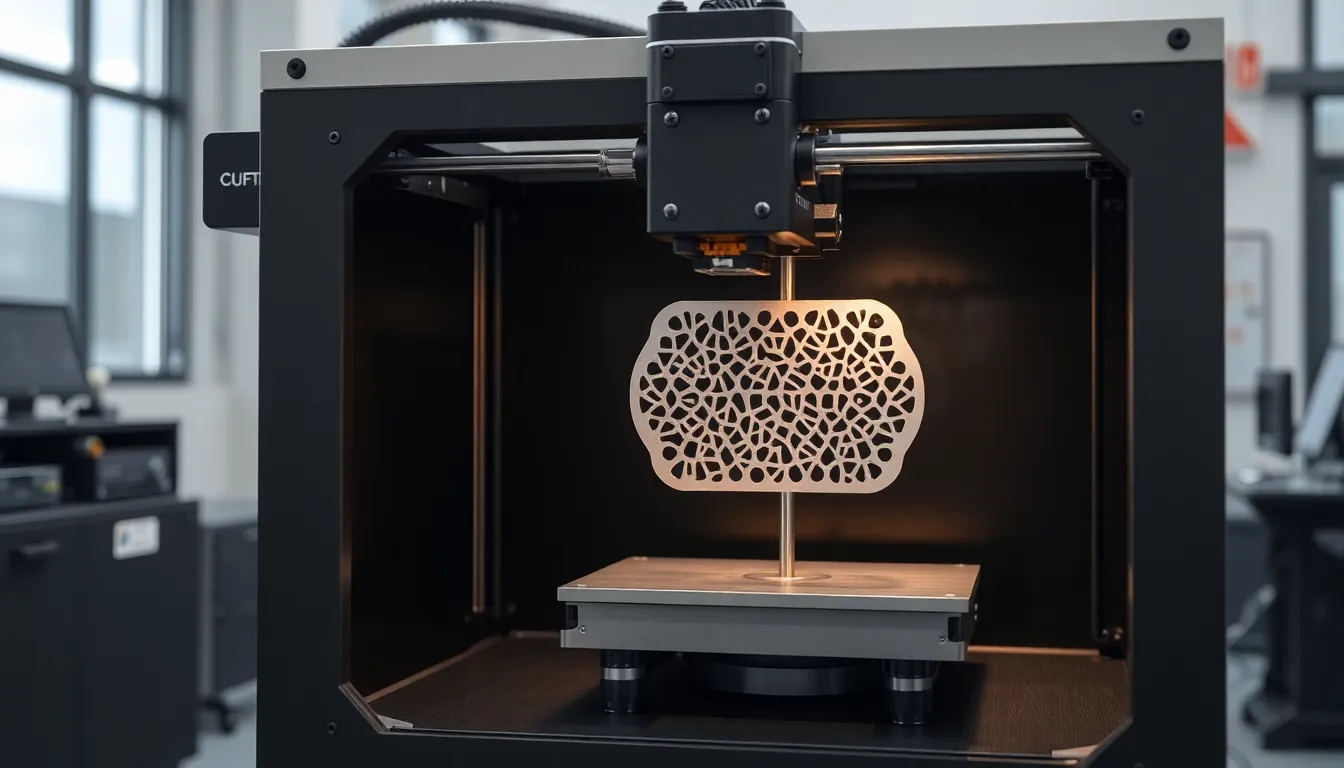
3D printing titanium offers significant advantages in various applications. The unique properties of titanium align perfectly with the capabilities of additive manufacturing.
Lightweight and Strong
Lightweight yet strong, titanium finds extensive use in critical applications. The high strength-to-weight ratio enables designers to create components that reduce overall weight without compromising strength. Industries like aerospace rely on these attributes for fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, titanium exhibits excellent fatigue resistance, extending the lifespan of components. This combination of features leads to improved efficiency throughout various applications.
Design Flexibility
Design flexibility stands out among the benefits of 3D printing titanium. Complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve become possible with additive manufacturing. Manufacturers can produce intricate structures with internal channels or lattice designs, optimizing material usage. Customization for specific applications becomes effortless, allowing tailored solutions for unique challenges. This adaptability opens up new avenues for innovation, enabling teams to meet evolving industry demands.
Applications of 3D Printing Titanium
3D printing titanium finds numerous applications across vital industries, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness. Two prominent fields include aerospace and medical implants.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace relies heavily on 3D printed titanium for manufacturing components. Parts like brackets, gears, and fuel nozzles emerge with high strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing performance. Designers create complex geometries, reducing aerodynamic drag and improving fuel efficiency. Reductions in material waste come from additive manufacturing techniques, which layer titanium powder precisely. Cost-effective solutions arise in production time, providing industries with competitive advantages. Companies leverage specific titanium alloys to meet rigorous standards, ensuring safety and performance in flight.
Medical Implants
Medical implants benefit significantly from the properties of 3D printed titanium. This material shines in devices such as titanium orthopedic implants and dental fixtures, where biocompatibility is crucial. Customized designs cater to individual patient needs, enhancing comfort and fit. Advanced manufacturing techniques enable the creation of intricate structures that promote osseointegration, leading to better healing outcomes. The lightweight nature of titanium helps reduce stress on surrounding tissues, a vital aspect in medical applications. 3D printing also accelerates the prototyping process, allowing rapid iterations for innovative healthcare solutions.
Challenges in 3D Printing Titanium
3D printing titanium presents notable challenges that impact production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Material Costs
Material costs for titanium powder remain high. Prices for titanium alloys often exceed those of conventional metals, such as aluminum or steel. The cost of Ti-6Al-4V, a popular titanium alloy, can reach $100 per kilogram. In comparison, traditional metals vary significantly in price, making titanium less accessible for some applications. Employers must evaluate budget constraints and project needs before opting for 3D printing with titanium. Despite its advantages, the investment in titanium powder requires thoughtful consideration.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations affect the widespread adoption of 3D printed titanium. Equipment for additive manufacturing, like selective laser melting machines, can be expensive and complex to operate. The layer thickness affects the final product’s resolution; thicker layers can lead to reduced detail. Thermal properties of titanium also pose challenges; warping and residual stress often occur during printing. Precision in control during the production process remains vital to avoid defects. Understanding these limitations helps industries navigate the complexities associated with 3D printing titanium.
Future Trends in 3D Printing Titanium
Advancements in 3D printing technology are reshaping titanium manufacturing, enabling the production of increasingly complex geometries. Innovations like hybrid manufacturing, which combines additive and subtractive techniques, enhance precision and efficiency. Emerging laser technologies improve processing speeds and reduce energy consumption, further refining the production process.
In the aerospace sector, expectations include the development of lightweight structures that meet stringent performance criteria. Companies are likely to pursue designs that minimize material usage while maximizing strength, benefiting aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. Customization capabilities will also expand, allowing for bespoke parts tailored to specific applications in real-time.
Medical applications are set to evolve as 3D printing titanium continues to gain traction. Optimizing biocompatibility through advanced titanium alloys can lead to better patient outcomes in orthopedic and dental implants. Personalized implants designed using patient imaging data will become more common, significantly improving fit and integration.
Cost reduction strategies will play a critical role in the future of 3D printing titanium. Manufacturers might explore sourcing and recycling titanium powder to lower expenses and enhance sustainability. As competition grows, advancements in production methods could make 3D printed titanium more accessible across various industries.
Training programs emphasizing additive manufacturing techniques will likely emerge. Engineers and technicians equipped with modern skills can effectively address challenges in 3D printing titanium and drive innovation. The continuous research into new alloys and materials presents opportunities for novel applications that may redefine industry standards.
The advancements in 3D printing titanium are reshaping industries by unlocking new possibilities in design and manufacturing. With its unique properties and the ability to create complex geometries, titanium is becoming increasingly vital in aerospace and medical applications. The ongoing challenges of high material costs and technical limitations are being addressed through innovative solutions and hybrid manufacturing techniques.
As technology continues to evolve, the future looks promising for 3D printed titanium. Companies that embrace these advancements will likely gain a competitive edge. By investing in training and research, industries can harness the full potential of this revolutionary manufacturing method, paving the way for more efficient and tailored solutions.